KPIs categories for Sustainability in Universities
At NTUA, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for sustainable development can be categorized according to type of sustainability. Below, the main thematic categories are listed along with indicative indicators that have been applied at the National Technical University of Athens (NTUA) and experiences are drawn from other European institutions.
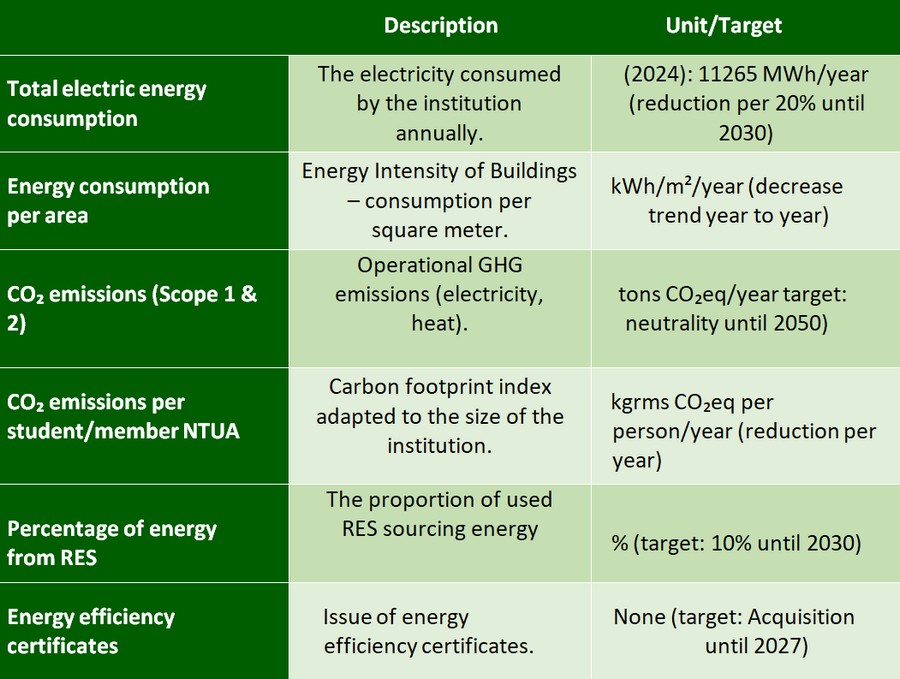
Energy consumption and CO₂ emissions reduction
The design and implementation of policies for sustainable energy management is a crucial pillar for NTUA. The main objective is to reduce energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions through energy efficiency initiatives, the use of renewable energy sources and the change of energy behaviors.
At NTUA, an electricity consumption monitoring system has been installed since 2015, with the installation of meters in all buildings of the Zografou campus and their expansion in three buildings of the Patission campus (2021). The collected data have allowed the creation of an energy consumption map and the analysis of the results for the formulation of policies. Indicatively, in the three-year period 2022-2024, a reduction in energy consumption of around 4% was achieved thanks to the replacement of old lighting fixtures with LED technology in the institution’s buildings.

Tbl 1. KPIs indicators for energy consumption and emissions reduction
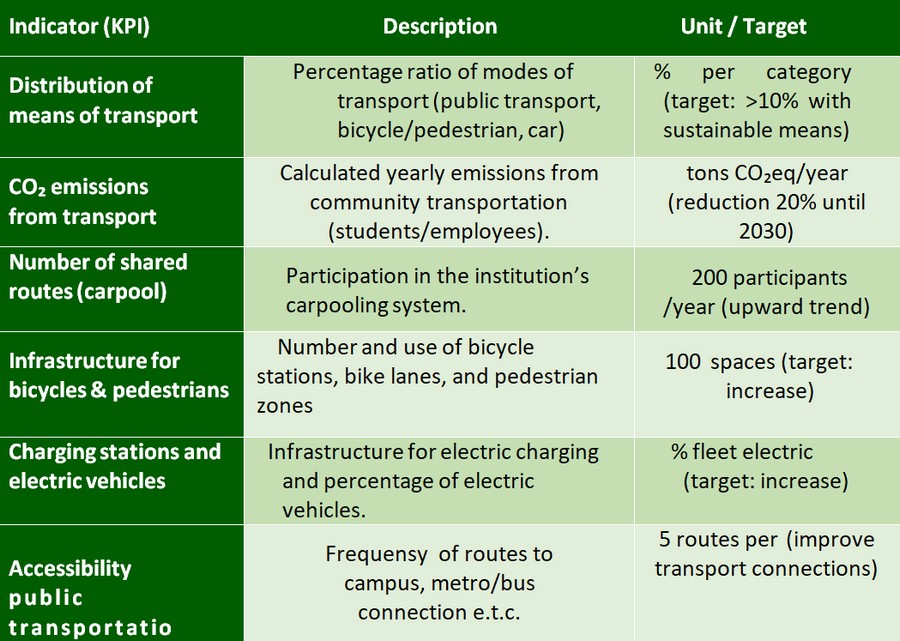
Sustainable transportation
The transport of students and staff to and from the Polytechnic University is an important source of indirect CO₂ emissions (Scope 3) and affects local traffic and the quality of life in the urban environment (SDG 11: Sustainable Cities & Communities). In addition, promoting sustainable mobility is essential to limit the use of private vehicles and encourage greener modes of transport such as public transport, cycling, hiking, as well as vehicle sharing or the use of electric means of transport.

At the National Technical University of Athens, the significant contribution of community member travel to annual carbon dioxide emissions is recognized, with the number of emissions amounting to thousand of tons. This fact makes these trips an important factor in the overall environment footprint of the institution and highlights the need for targeted interventions.

Tbl. 2. KPIs indicators for sustainable transport
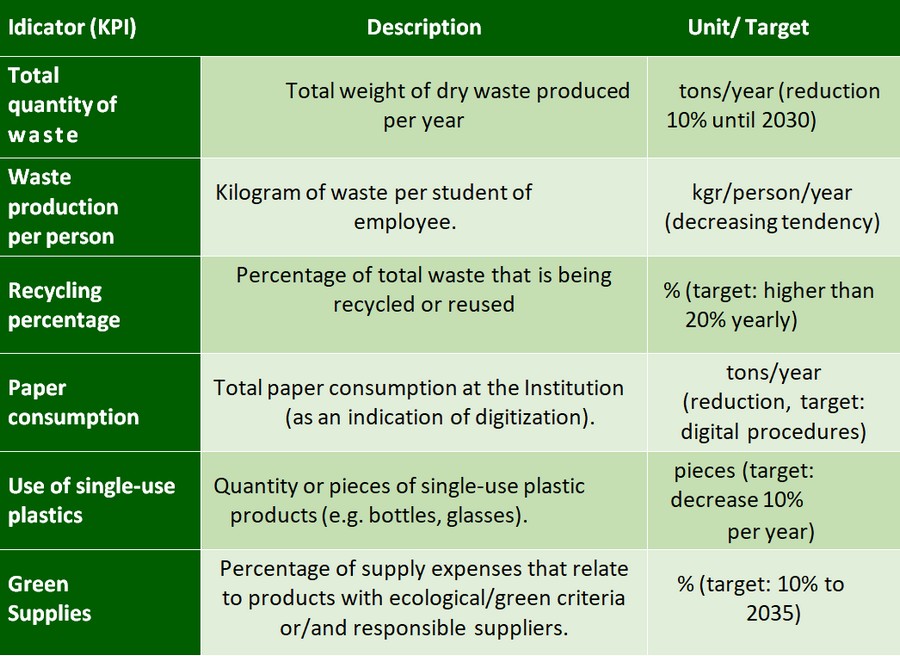
Waste management and circular economy
Effective waste management and the implementation of circular economy principles are essential priorities for achieving a sustainable university environment, contributing to the implementation of Sustainable Development Goal 12 for Responsible Consumption and Production. Universities, as major waste producers, face the challenge of reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills through practices such as reduction, reuse and recycling, as well as through the management of electronic and hazardous waste.
At National Technical University of Athens, a comprehensive plan for the reduction, sorting and effective management of waste on campus is being implemented. The program includes the installation of recycling bins in all areas, the collaboration with specialized bodies for the recycling of special waste, such as batteries and electrical and electronic devices, as well as campaigns to reduce the use of single-use plastics in canteens, such as cups and straws.

At the same time, the green procurement policy of the National Technical University of Athens is at the heart of the strategy for sustainable development with the aim of reducing the institution’s ecological footprint in the future.
Tbl. 3. Indicators KPIs for waste and circular economy
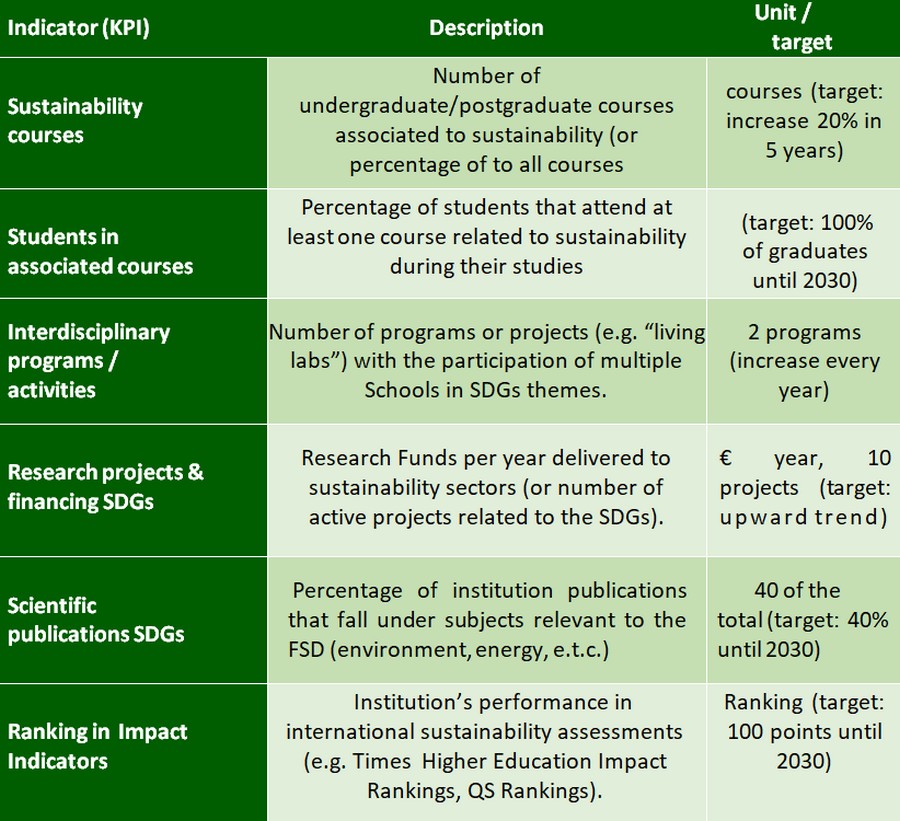
Education and Research for Sustainability

The integration of sustainability principles in academic and research activity is a central objective for universities seeking to actively contribute to the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals, especially in the field of quality education and innovation. The KPIs in this area record the impact that the university has on the training of professionals and the production of knowledge capable of supporting the application of the principles of sustainable development in society.

Αt National Technical University of Athens, the contribution to sustainable development is shaped through a series of specialized courses covering a full range of topics. The educational approach seeks to integrate these courses into all faculties, encouraging students to understand and apply this knowledge to their subjects of study. For example, at the School of Civil Engineering, the course “Environmental “Impacts” teaches techniques for the assessment and management of the environmental impacts of engineering projects, while the School of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering offers courses that analyze smart buildings, smart cities, heat pumps of alternative refrigerants, anti-pollution technologies, the use of renewable energy sources, etc.
Beyond the educational sector, the Technical University actively participates in research projects related to sustainable development, taking advantage of national and European funding to promote research in sustainable technologies and climate change.
Tbl. 4. KPIs indicators on education & research on Sustainability